| Affected Part |
|
Summary |
|
|
Taxon |
Vernacular |
Classification |
References |
Darwin Classification of Active Taxon |
Active Taxon |
Active Vernacular |
Active Taxon Uncertain |
Active State |
Active Part |
Active Stage |
Relationship |
Relationship Uncertain |
Relationship Geography |
Darwin Classification of Passive Taxon |
Passive Taxon |
Passive Vernacular |
Passive Taxon Uncertain |
Passive State |
Passive Part |
Passive Stage |
Passive Taxon's significance to Active Taxon |
Indoors etc |
Season |
Summary |
|
|
may be infected and damaged by |
|
 |
Armillaria |
honey fungi |
Agaricales: Physalacriaceae |
British Parasitic Fungi, Moore, W.C., 1959
|
/Fungi/Basidiomycota/Agaricomycetes/Agaricales/Physalacriaceae/Armillaria/ | Armillaria | honey fungi | | | | |
Foodplant / pathogen | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | | | | |
| | infects and damages |
| bark (dead) |
|
dead bark is decayed by scattered, immersed, up to 2mm diam. stroma of Cytospora coelomycetous anamorph |
 |
|
Cytospora pini |
a stromatic coelomycete |
Diaporthales: Valsaceae |
British Stem- and Leaf- Fungi: Coelomycetes Vol. I … Sphaeropsidales with hyaline conidia, Grove, W.B., 1935
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Sordariomycetes/Diaporthales/Valsaceae/Cytospora pini/ | Cytospora pini | a stromatic coelomycete | | scattered, immersed, up to 2mm diam. | stroma | Cytospora coelomycetous anamorph |
Foodplant / saprobe | | Foreign |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead | bark | | |
| | scattered, immersed, up to 2mm diam. stroma of Cytospora coelomycetous anamorph is saprobic on dead bark |
| bark (live) |
|
live bark has sap sucked by |
|
|
Pineus strobi |
Weymouth Pine Adelgid, Pine Bark Adelgid |
Hemiptera: Adelgidae |
Pests, Diseases & Disorders of Garden Plants, Buczacki, S. & Harris, K., 1998
|
/Animalia/Arthropoda/Insecta/Hemiptera/Adelgidae/Pineus strobi/ | Pineus strobi | Weymouth pine adelgid, pine bark adelgid | | | | |
Foodplant / sap sucker | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | live | bark | | |
| (1-12) | sucks sap of live bark |
| branch (small) (brittle, dead, attached, lacking needles) |
|
brittle, dead, attached, lacking needles branch (small) is decayed by immersed apothecium |
|
|
Therrya pini |
an ascomycete fungus |
Rhytismatales: Rhytismataceae |
Therrya pini (Alb. & Schwein.) Höhn., Minter, D.W., 1996
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Leotiomycetes/Rhytismatales/Rhytismataceae/Therrya pini/ | Therrya pini | an ascomycete fungus | | immersed | | apothecium |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | brittle, dead, attached, lacking needles | branch (small) | | |
| (2-7) | immersed apothecium is saprobic on brittle, dead, attached, lacking needles branch (small) |
| branch (small) (brittle, dead, fallen, lacking needles) |
|
brittle, dead, fallen, lacking needles branch (small) is decayed by immersed apothecium |
|
|
Therrya pini |
an ascomycete fungus |
Rhytismatales: Rhytismataceae |
Therrya pini (Alb. & Schwein.) Höhn., Minter, D.W., 1996
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Leotiomycetes/Rhytismatales/Rhytismataceae/Therrya pini/ | Therrya pini | an ascomycete fungus | | immersed | | apothecium |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | brittle, dead, fallen, lacking needles | branch (small) | | |
| (2-7) | immersed apothecium is saprobic on brittle, dead, fallen, lacking needles branch (small) |
| branch (dead, fallen) |
|
dead, fallen branch is decayed by erumpent, solitary or clustered apothecium |
|
|
Pezicula livida |
a discomycete |
Helotiales: Dermateaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Leotiomycetes/Helotiales/Dermateaceae/Pezicula livida/ | Pezicula livida | a discomycete | | erumpent, solitary or clustered | | apothecium |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead, fallen | branch | | |
| (1-12) | erumpent, solitary or clustered apothecium is saprobic on dead, fallen branch |
| branch (dead, fallen) |
|
dead, fallen branch is decayed by Cryptosporiopsis anamorph |
|
|
Pezicula livida |
a discomycete |
Helotiales: Dermateaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Leotiomycetes/Helotiales/Dermateaceae/Pezicula livida/ | Pezicula livida | a discomycete | | | | Cryptosporiopsis anamorph |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead, fallen | branch | | |
| | Cryptosporiopsis anamorph is saprobic on dead, fallen branch |
| branch (dead) |
|
dead branch is decayed by erumpent stroma |
|
|
Neonectria fuckeliana |
a pyrenomycete |
Hypocreales: Nectriaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Sordariomycetes/Hypocreales/Nectriaceae/Neonectria fuckeliana/ | Neonectria fuckeliana | a pyrenomycete | | erumpent | | stroma |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead | branch | | |
| (3-5, 9-12) | erumpent stroma is saprobic on dead branch |
| branch (dead) |
|
dead branch is decayed by multilocular conidioma of Zythiostroma coelomycetous anamorph |
|
|
Neonectria fuckeliana |
a pyrenomycete |
Hypocreales: Nectriaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Sordariomycetes/Hypocreales/Nectriaceae/Neonectria fuckeliana/ | Neonectria fuckeliana | a pyrenomycete | | multilocular | conidioma | Zythiostroma coelomycetous anamorph |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead | branch | | |
| | multilocular conidioma of Zythiostroma coelomycetous anamorph is saprobic on dead branch |
| branch (dead) |
|
dead branch is decayed by stromatic, in large groups perithecium |
|
|
Neonectria fuckeliana |
a pyrenomycete |
Hypocreales: Nectriaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Sordariomycetes/Hypocreales/Nectriaceae/Neonectria fuckeliana/ | Neonectria fuckeliana | a pyrenomycete | | stromatic, in large groups | | perithecium |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead | branch | | |
| (3-5, 9-12) | stromatic, in large groups perithecium is saprobic on dead branch |
| branch (old, dead, decorticate) |
|
old, dead, decorticate branch is decayed by fruitbody |
 |
|
Xylobolus frustulatus |
a basidiomycete fungus |
Russulales: Stereaceae |
Contribution to chorology of Xylobolus frustulatus in Poland, Stasinska, M., 2008
|
/Fungi/Basidiomycota/Agaricomycetes/Russulales/Stereaceae/Xylobolus frustulatus/ | Xylobolus frustulatus | a basidiomycete fungus | | | | fruitbody |
Foodplant / saprobe | | Foreign |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | old, dead, decorticate | branch | | |
| | fruitbody is saprobic on old, dead, decorticate branch |
| cone scale |
|
cone scale is foodplant of gregarious, subepidermal then erumpent through cleft epidermis, dull black pycnidium of Diplodina coelomycetous anamorph |
 |
|
Diplodina strobi |
a coelomycete |
Diaporthales: Gnomoniaceae |
British Stem- and Leaf- Fungi: Coelomycetes Vol. I … Sphaeropsidales with hyaline conidia, Grove, W.B., 1935
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Sordariomycetes/Diaporthales/Gnomoniaceae/Diplodina strobi/ | Diplodina strobi | a coelomycete | | gregarious, subepidermal then erumpent through cleft epidermis, dull black | pycnidium | Diplodina coelomycetous anamorph |
Foodplant / feeds on | | UK and/or Eire |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | | cone scale | | |
| (1-5) | gregarious, subepidermal then erumpent through cleft epidermis, dull black pycnidium of Diplodina coelomycetous anamorph feeds on cone scale |
| cone (dead, fallen) |
|
dead, fallen cone is decayed by erumpent, solitary or clustered apothecium |
|
|
Pezicula livida |
a discomycete |
Helotiales: Dermateaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Leotiomycetes/Helotiales/Dermateaceae/Pezicula livida/ | Pezicula livida | a discomycete | | erumpent, solitary or clustered | | apothecium |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead, fallen | cone | | |
| (1-12) | erumpent, solitary or clustered apothecium is saprobic on dead, fallen cone |
| cone (dead, fallen) |
|
dead, fallen cone is decayed by Cryptosporiopsis anamorph |
|
|
Pezicula livida |
a discomycete |
Helotiales: Dermateaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Leotiomycetes/Helotiales/Dermateaceae/Pezicula livida/ | Pezicula livida | a discomycete | | | | Cryptosporiopsis anamorph |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead, fallen | cone | | |
| | Cryptosporiopsis anamorph is saprobic on dead, fallen cone |
| leaf (dead) |
|
dead leaf is decayed by erumpent stroma |
 |
|
Neonectria fuckeliana |
a pyrenomycete |
Hypocreales: Nectriaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Sordariomycetes/Hypocreales/Nectriaceae/Neonectria fuckeliana/ | Neonectria fuckeliana | a pyrenomycete | | erumpent | | stroma |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead | leaf | | Minor |
| (3-5, 9-12) | erumpent stroma is saprobic on dead leaf |
| leaf (dead) |
|
dead leaf is decayed by multilocular conidioma of Zythiostroma coelomycetous anamorph |
 |
|
Neonectria fuckeliana |
a pyrenomycete |
Hypocreales: Nectriaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Sordariomycetes/Hypocreales/Nectriaceae/Neonectria fuckeliana/ | Neonectria fuckeliana | a pyrenomycete | | multilocular | conidioma | Zythiostroma coelomycetous anamorph |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead | leaf | | Minor |
| | multilocular conidioma of Zythiostroma coelomycetous anamorph is saprobic on dead leaf |
| leaf (dead) |
|
dead leaf is decayed by stromatic, in large groups perithecium |
 |
|
Neonectria fuckeliana |
a pyrenomycete |
Hypocreales: Nectriaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Sordariomycetes/Hypocreales/Nectriaceae/Neonectria fuckeliana/ | Neonectria fuckeliana | a pyrenomycete | | stromatic, in large groups | | perithecium |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead | leaf | | Minor |
| (3-5, 9-12) | stromatic, in large groups perithecium is saprobic on dead leaf |
| leaf (live, slightly discoloured) |
|
live, slightly discoloured leaf has sap sucked by |
|
|
Pineus strobi |
Weymouth Pine Adelgid, Pine Bark Adelgid |
Hemiptera: Adelgidae |
Pests, Diseases & Disorders of Garden Plants, Buczacki, S. & Harris, K., 1998
|
/Animalia/Arthropoda/Insecta/Hemiptera/Adelgidae/Pineus strobi/ | Pineus strobi | Weymouth pine adelgid, pine bark adelgid | | | | |
Foodplant / sap sucker | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | live, slightly discoloured | leaf | | |
| (1-12) | sucks sap of live, slightly discoloured leaf |
| log (old, dead, decorticate) |
 |
old, dead, decorticate log is decayed by fruitbody |
 |
|
Xylobolus frustulatus |
a basidiomycete fungus |
Russulales: Stereaceae |
Contribution to chorology of Xylobolus frustulatus in Poland, Stasinska, M., 2008
|
/Fungi/Basidiomycota/Agaricomycetes/Russulales/Stereaceae/Xylobolus frustulatus/ | Xylobolus frustulatus | a basidiomycete fungus | | | | fruitbody |
Foodplant / saprobe | | Foreign |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | old, dead, decorticate | log | | |
| | fruitbody is saprobic on old, dead, decorticate log |
| needle |
|
needle is foodplant of gregarious, subepidermal then erumpent through cleft epidermis, dull black pycnidium of Diplodina coelomycetous anamorph |
  |
|
Diplodina strobi |
a coelomycete |
Diaporthales: Gnomoniaceae |
British Stem- and Leaf- Fungi: Coelomycetes Vol. I … Sphaeropsidales with hyaline conidia, Grove, W.B., 1935
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Sordariomycetes/Diaporthales/Gnomoniaceae/Diplodina strobi/ | Diplodina strobi | a coelomycete | | gregarious, subepidermal then erumpent through cleft epidermis, dull black | pycnidium | Diplodina coelomycetous anamorph |
Foodplant / feeds on | | UK and/or Eire |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | ? | | needle | | |
| (1-5) | gregarious, subepidermal then erumpent through cleft epidermis, dull black pycnidium of Diplodina coelomycetous anamorph feeds on needle |
| needle (live, brown-spotted) |
|
live, brown-spotted needle may be infected and damaged by subepidermal, then exposed, mainly hypophyllous apothecium |
|
|
Meloderma desmazieri |
a discomycete |
Rhytismatales: Rhytismataceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
Meloderma desmazieresii, Minter, D.W. & Gibson, I.A.S., 1998
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Leotiomycetes/Rhytismatales/Rhytismataceae/Meloderma desmazieri/ | Meloderma desmazieri | a discomycete | | subepidermal, then exposed, mainly hypophyllous | | apothecium |
Foodplant / pathogen | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | live, brown-spotted | needle | | |
| | subepidermal, then exposed, mainly hypophyllous apothecium infects and damages live, brown-spotted needle |
| needles |
|
needles is grazed by web-dwelling communal larva |
  |
|
Acantholyda erythrocephala |
Red-headed Pine Spinner |
Hymenoptera: Pamphiliidae |
Hymenoptera: 2. Symphyta. Section (a), Benson, R.B., 1951
|
/Animalia/Arthropoda/Insecta/Hymenoptera/Pamphiliidae/Acantholyda erythrocephala/ | Acantholyda erythrocephala | red-headed pine spinner | | communal | | larva |
Foodplant / web feeder | | Foreign |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | | needles | | Major |
| | communal larva feeds from web on needles |
| root (live) |
|
live root is ectomycorrhizal host of fruitbody |
 |
|
Suillus placidus |
Slippery White Bolete |
Boletales: Suillaceae |
Checklist of the British and Irish Basidiomycota, Legon, N.W. & Henrici, A. with Roberts, P.J., Spooner, B.M. & Watling, R., 2005
Boletes and their allies, Watling, R., Hills, A.E, & Turnbull, E., 2005
|
/Fungi/Basidiomycota/Agaricomycetes/Boletales/Suillaceae/Suillus placidus/ | Suillus placidus | slippery white bolete | | | | fruitbody |
Foodplant / mycorrhiza / ectomycorrhiza | | UK and/or Eire |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | live | root | | |
| | fruitbody is ectomycorrhizal with live root |
| root (live) |
|
live root is ectomycorrhizal host of fruitbody |
  |
 |
Thelephora terrestris |
Earthfan |
Thelephorales: Thelephoraceae |
Mycorrhizal fungi, Watling, R., 1980
|
/Fungi/Basidiomycota/Agaricomycetes/Thelephorales/Thelephoraceae/Thelephora terrestris/ | Thelephora terrestris | earthfan | | | | fruitbody |
Foodplant / mycorrhiza / ectomycorrhiza | | UK and/or Eire |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | live | root | | |
Indoors, in greenhouse, captivity, culture or experimentally induced | | fruitbody is ectomycorrhizal with live root |
| shoot (live) |
|
live shoot has sap sucked by |
|
|
Pineus strobi |
Weymouth Pine Adelgid, Pine Bark Adelgid |
Hemiptera: Adelgidae |
Pests, Diseases & Disorders of Garden Plants, Buczacki, S. & Harris, K., 1998
|
/Animalia/Arthropoda/Insecta/Hemiptera/Adelgidae/Pineus strobi/ | Pineus strobi | Weymouth pine adelgid, pine bark adelgid | | | | |
Foodplant / sap sucker | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | live | shoot | | |
| (1-12) | sucks sap of live shoot |
| stem |
|
stem may be infected and damaged by erumpent aecium |
 |
 |
Cronartium ribicola |
White Pine Blister Rust |
Pucciniales: Cronartiaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
British Parasitic Fungi, Moore, W.C., 1959
British Rust Fungi, Wilson, M., & Henderson, D., 1966
|
/Fungi/Basidiomycota/Pucciniomycetes/Pucciniales/Cronartiaceae/Cronartium ribicola/ | Cronartium ribicola | white pine blister rust | | erumpent | | aecium |
Foodplant / pathogen | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | | stem | | Major |
| (3-6) | erumpent aecium infects and damages stem |
| stem |
|
stem may be infected and damaged by subcortical pycnium |
 |
 |
Cronartium ribicola |
White Pine Blister Rust |
Pucciniales: Cronartiaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
British Rust Fungi, Wilson, M., & Henderson, D., 1966
|
/Fungi/Basidiomycota/Pucciniomycetes/Pucciniales/Cronartiaceae/Cronartium ribicola/ | Cronartium ribicola | white pine blister rust | | subcortical | | pycnium |
Foodplant / pathogen | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | | stem | | Major |
| (3-6) | subcortical pycnium infects and damages stem |
| stump (old, dead, decorticate) |
|
old, dead, decorticate stump is decayed by fruitbody |
 |
|
Xylobolus frustulatus |
a basidiomycete fungus |
Russulales: Stereaceae |
Contribution to chorology of Xylobolus frustulatus in Poland, Stasinska, M., 2008
|
/Fungi/Basidiomycota/Agaricomycetes/Russulales/Stereaceae/Xylobolus frustulatus/ | Xylobolus frustulatus | a basidiomycete fungus | | | | fruitbody |
Foodplant / saprobe | | Foreign |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | old, dead, decorticate | stump | | |
| | fruitbody is saprobic on old, dead, decorticate stump |
| stump (weathered) |
|
weathered stump is decayed by hysterothecium |
 |
|
Mytilinidion scolecosporum |
an ascomycete |
Mytilinidiales: Mytilinidiaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Dothideomycetes/Mytilinidiales/Mytilinidiaceae/Mytilinidion scolecosporum/ | Mytilinidion scolecosporum | an ascomycete | | | | hysterothecium |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | weathered | stump | | Major |
| | hysterothecium is saprobic on weathered stump |
| twig (brittle, recently dead, attached) |
|
brittle, recently dead, attached twig is decayed by erumpent apothecium |
 |
|
Coccomyces strobi |
|
Rhytismatales: Rhytismataceae |
Coccomyces strobi J. Reid & Cain, Minter, D.W., 1996
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Leotiomycetes/Rhytismatales/Rhytismataceae/Coccomyces strobi/ | Coccomyces strobi | | | erumpent | | apothecium |
Foodplant / saprobe | | Foreign |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | brittle, recently dead, attached | twig | | |
| | erumpent apothecium is saprobic on brittle, recently dead, attached twig |
| twig (dead) |
|
dead twig is decayed by immersed, grouped perithecium |
|
|
Valsa pini |
a valsoid pyrenomycete |
Diaporthales: Valsaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Sordariomycetes/Diaporthales/Valsaceae/Valsa pini/ | Valsa pini | a valsoid pyrenomycete | | immersed, grouped | | perithecium |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead | twig | | |
| (11-2) | immersed, grouped perithecium is saprobic on dead twig |
| twig (dead) |
|
dead twig is decayed by erumpent stroma |
|
|
Neonectria fuckeliana |
a pyrenomycete |
Hypocreales: Nectriaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Sordariomycetes/Hypocreales/Nectriaceae/Neonectria fuckeliana/ | Neonectria fuckeliana | a pyrenomycete | | erumpent | | stroma |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead | twig | | |
| (3-5, 9-12) | erumpent stroma is saprobic on dead twig |
| twig (dead) |
|
dead twig is decayed by multilocular conidioma of Zythiostroma coelomycetous anamorph |
|
|
Neonectria fuckeliana |
a pyrenomycete |
Hypocreales: Nectriaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Sordariomycetes/Hypocreales/Nectriaceae/Neonectria fuckeliana/ | Neonectria fuckeliana | a pyrenomycete | | multilocular | conidioma | Zythiostroma coelomycetous anamorph |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead | twig | | |
| | multilocular conidioma of Zythiostroma coelomycetous anamorph is saprobic on dead twig |
| twig (dead) |
|
dead twig is decayed by stromatic, in large groups perithecium |
|
|
Neonectria fuckeliana |
a pyrenomycete |
Hypocreales: Nectriaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Sordariomycetes/Hypocreales/Nectriaceae/Neonectria fuckeliana/ | Neonectria fuckeliana | a pyrenomycete | | stromatic, in large groups | | perithecium |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead | twig | | |
| (3-5, 9-12) | stromatic, in large groups perithecium is saprobic on dead twig |
| twig (dead) |
|
dead twig is decayed by immersed, becoming erumpeny conidioma of Strasseria coelomycetous anamorph |
|
|
Strasseria geniculata |
a coelomycete |
|
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Strasseria geniculata/ | Strasseria geniculata | a coelomycete | | immersed, becoming erumpeny | conidioma | Strasseria coelomycetous anamorph |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | dead | twig | | |
| (1-5) | immersed, becoming erumpeny conidioma of Strasseria coelomycetous anamorph is saprobic on dead twig |
| twig (live) |
|
live twig may be infected and damaged by Brunchorstia anamorph |
 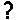 |
|
Gremmeniella abietina |
Pine Die-back - causative organism |
Helotiales: Godroniaceae |
British Parasitic Fungi, Moore, W.C., 1959
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Leotiomycetes/Helotiales/Godroniaceae/Gremmeniella abietina/ | Gremmeniella abietina | pine die-back (causative organism) | | | | Brunchorstia anamorph |
Foodplant / pathogen | | UK and/or Eire |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | ? | live | twig | | |
| | Brunchorstia anamorph infects and damages live twig |
| wood |
|
wood is decayed by hysterothecium |
 |
|
Mytilinidion scolecosporum |
an ascomycete |
Mytilinidiales: Mytilinidiaceae |
Microfungi on Land Plants: An Identification Handbook, Ellis, M.B. & J.P., 1997
|
/Fungi/Ascomycota/Dothideomycetes/Mytilinidiales/Mytilinidiaceae/Mytilinidion scolecosporum/ | Mytilinidion scolecosporum | an ascomycete | | | | hysterothecium |
Foodplant / saprobe | | |
/Plantae/Tracheophyta/Pinopsida/Pinales/Pinaceae/Pinus strobus/ | Pinus strobus | Weymouth pine, eastern white pine | | | wood | | Major |
| | hysterothecium is saprobic on wood |



















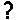
 NBN (data.nbn.org.uk)
NBN (data.nbn.org.uk)